
 Language
▼
Language
▼
More Language

In the fields of fine chemicals and materials industry, petroleum resin, as an important by-product based thermoplastic resin, is widely used in various industries such as adhesives, coatings, rubber, inks, road marking paints, etc. due to its excellent viscosity, water resistance, weather resistance, and compatibility. However, this high-performance material has a series of strict and special requirements for storage conditions in the warehousing and logistics process before its final application. Neglecting these requirements not only leads to qualitative changes and performance degradation of petroleum resin products, resulting in direct economic losses, but also may cause serious safety and environmental accidents. Therefore, a deep understanding and strict implementation of its special storage regulations is an important issue that runs through the petroleum resin industry chain.

Temperature is the primary factor affecting the stability of petroleum resin. The vast majority of petroleum resins are solid block, flake or granular at room temperature, and their softening point varies depending on the type (such as C5, C9, hydrogenated petroleum resins, etc.), usually between 80 ° C and 140 ° C. This characteristic determines the two core principles of storage temperature management:
1. Prevent high temperature melting and agglomeration: The temperature of the storage environment must be strictly below the softening point of petroleum resin. If the ambient temperature is too high, approaching or exceeding its softening point, the resin will begin to soften and become sticky, leading to particles or flakes sticking to each other and forming huge, difficult to separate hard blocks. This not only makes subsequent retrieval and feeding extremely difficult, requiring additional crushing processes, increasing labor and energy costs, but also leads to local aging due to uneven heating, affecting its molecular structure and final performance. Therefore, the warehouse must have good ventilation and insulation performance. In hot seasons or areas, it is even necessary to use air conditioning or forced ventilation systems to control the temperature within a safe range (usually recommended below 40 ° C).3. Delaying thermal oxidation aging: Petroleum resins, especially the unhydrogenated C9 series, contain unsaturated double bonds in their molecular structure and are sensitive to heat and oxygen. Long term exposure to high temperature environments, even if the softening point has not been reached, can accelerate its thermal oxidation reaction with oxygen in the air, leading to color darkening (yellowing), increased acid value, and decreased adhesion performance. Therefore, constant and suitable low-temperature storage is the key to maintaining the light color and stable performance of petroleum resin.

3. Packaging and storage measures: Therefore, petroleum resin must be stored in a dry and ventilated indoor environment, with a relative humidity preferably controlled below 70%. The packaging must use double-layer or even multi-layer moisture-proof packaging, with the inner layer being a polyethylene film bag and the outer layer being a woven bag or paper plastic composite bag to ensure good sealing. It is absolutely prohibited to transport or temporarily stack in the open air at the dock. The warehouse floor should be covered with pallets to isolate the goods from the ground and prevent moisture from entering.
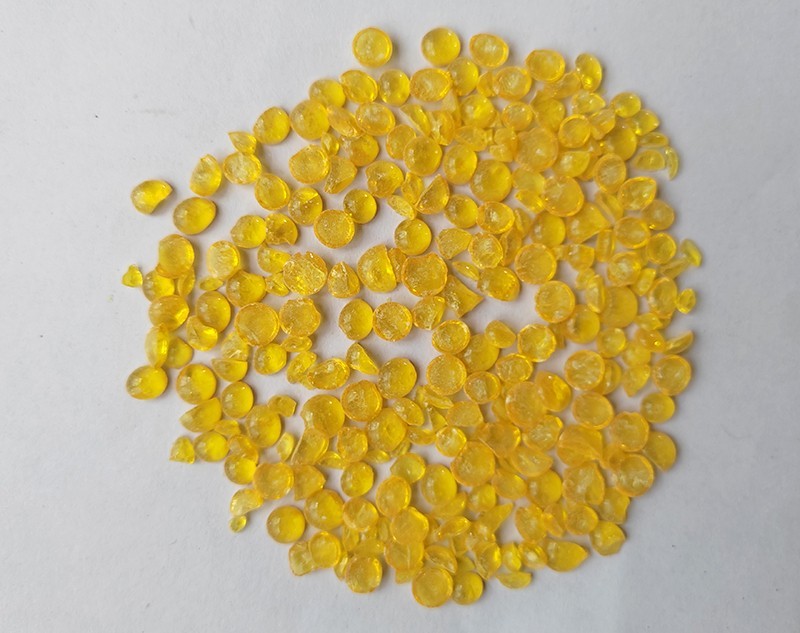

3. Comprehensive fire-fighting facilities: The warehouse should be equipped with sufficient and suitable fire-fighting equipment, such as dry powder fire extinguishers, carbon dioxide fire extinguishers, etc., and ensure that they are in effective condition. At the same time, there should be unobstructed fire exits and emergency evacuation plans.
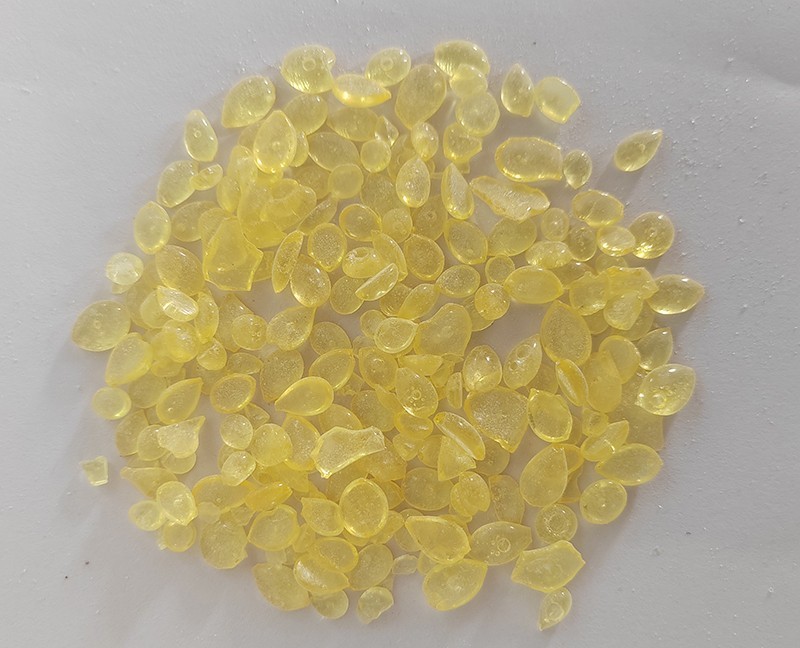

2. Scientific stacking method: The inventory management principle of "first in, first out" (FIFO) should be followed to avoid products exceeding their shelf life due to long-term backlog. The stacking height should be reasonably set according to the load-bearing capacity of the packaging bag and the properties of the petroleum resin (granular has better pressure resistance, followed by flake), to prevent the lower layer of goods from clumping due to excessive pressure. There should be sufficient spacing between piles and between piles and walls to facilitate ventilation, inspection, and firefighting operations.
 Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province
Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com
E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com WhatsApp:+8615053337101
WhatsApp:+8615053337101
China C5 hydrogenated petroleum resin supplier : Shangdong Wanbang New Materials Co., Ltd.
C5 hydrocarbon resin manufacturer has a wide range of applications, high quality, low price, and multiple uses.Welcome to consult.