In industrial production,
C5 petroleum resin is widely used in adhesives,coatings,rubber,inks,and other fields due to its excellent tackifying,water resistance,and acid and alkali resistance properties.However,to make this solid resin effective,it must first be dissolved into a liquid state suitable for processing.Selecting the appropriate solvent is not arbitrary;it follows the classic chemical principle of"like dissolves like."C5 resin is essentially a non-polar or weakly polar hydrocarbon polymer,so it is easily soluble in non-polar or weakly polar solvents with similar chemical properties.
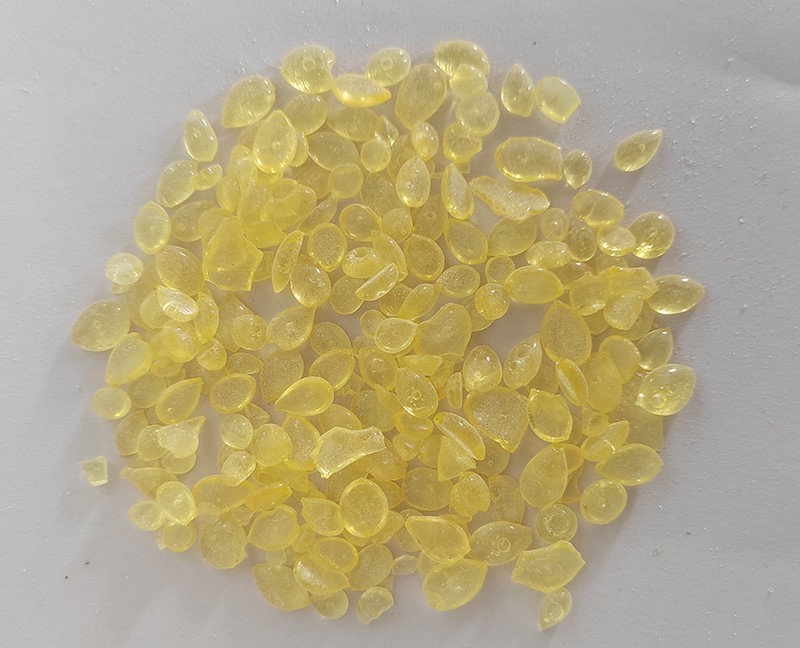

Currently,the most commonly used and cost-effective solvents in industry are aliphatic hydrocarbons,such as the commonly available 200#solvent naphtha.These solvents have a relatively mild odor,low toxicity,and significant cost advantages,making them the preferred choice for many general-purpose adhesive and coating formulations.When stronger dissolving power is required to prepare solutions with higher solid content or lower viscosity,aromatic hydrocarbon solvents like xylene and toluene have traditionally served as the mainstay.They can quickly and thoroughly dissolve the resin,providing excellent processing performance.However,it is important to note that aromatic hydrocarbon solvents are highly volatile,have a pungent odor,and pose greater potential impacts on health and the environment.Therefore,with increasingly stringent environmental regulations today,their use is facing growing restrictions.
In addition to hydrocarbons,ester solvents such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate also demonstrate good dissolving capabilities.Their odor characteristics differ from those of hydrocarbons,and their evaporation rates are adjustable.In certain specific formulations,they are used to regulate drying speed or improve compatibility with other polar components,serving as important functional supplements.Furthermore,solvents like cyclohexane,which belong to the naphthenic hydrocarbon category,offer better dissolving power than ordinary aliphatic hydrocarbons while being less toxic than aromatic hydrocarbons,presenting a favorable compromise.
The choice of solvent for C5 petroleum resin ultimately depends on the specific application scenario and comprehensive considerations.For example,in manufacturing pressure-sensitive adhesive tapes,faster-evaporating solvents may be required to facilitate drying,whereas in producing rubber compounds for tires,direct combination with process oils might be used.In contemporary times,environmental protection and safety have become decisive factors that cannot be ignored.Traditional aromatic hydrocarbon solvents are gradually being replaced by greener and safer dearomatized aliphatic hydrocarbon solvents.These solvents,through deep removal of aromatic components,retain good dissolving power while significantly reducing toxicity and odor.They comply with increasingly stringent VOC emission standards and represent the major trend for the future.
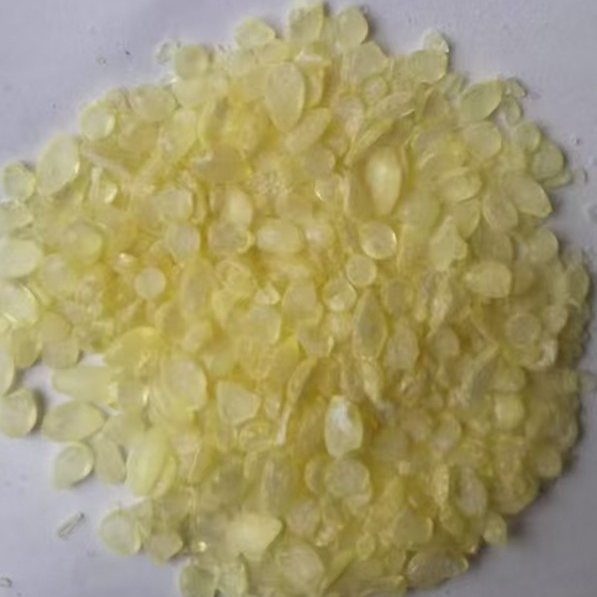

In summary,dissolving C5 petroleum resin is not a challenge,but optimizing solvent selection is an art of balance.It requires finding the optimal balance among dissolving efficiency,evaporation rate,production cost,processing technology,and,most importantly,environmental and safety regulations.From the classic and readily available 200#solvent naphtha and xylene to the promising eco-friendly dearomatized aliphatic hydrocarbon solvents,the correct choice is the first step in ensuring excellent product performance and meeting the requirements of the times.

 Language
▼
Language
▼



 Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province
Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com
E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com WhatsApp:+8615053337101
WhatsApp:+8615053337101