C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin, as an important derivative of petrochemicals, is not a stable substance that can be stored freely due to its physical and chemical properties. Strict storage conditions are a key prerequisite for maintaining specific performance indicators at the time of leaving the factory and ensuring downstream product quality and production safety. Any deviation from the prescribed storage requirements - whether it is temperature, humidity, fire source management, or packaging sealing - may trigger a series of chain deterioration from micro molecular structure to macro application performance, and even lead to serious safety accidents. A deep understanding of these specific consequences is of great significance for guiding warehouse management, avoiding economic risks, and ensuring production safety.
1. Physical state changes and performance degradation
This is the most direct and common consequence of not meeting storage conditions, which directly affects the processability of the best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin and the quality of the final product.
1. Agglomeration and melting
(1) Cause: Storage temperature is the core factor. As a thermoplastic material, the glass transition temperature and softening point of resin determine its sensitivity to temperature.
-Excessive temperature: If the storage environment temperature continues or intermittently exceeds the softening point of the resin (usually between 80 ° C-140 ° C, depending on the grade), the best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin particles or blocks will begin to soften, become sticky, and then melt and adhere. Inside the packaging bag, particles will adhere to each other, forming huge hard blocks. For bulk resin, it may cause the entire stack to become compacted.
-Temperature fluctuations: Repeated temperature differences between day and night or alternating between cold and warm can cause the C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin to undergo a "cold flow" phenomenon, which means repeated softening and hardening at the microscopic level, ultimately leading to the disappearance of particle boundaries and the formation of a whole.
(2) Specific consequences:
-Difficulty in retrieval: After agglomeration, normal pipeline pneumatic conveying or mechanical feeding cannot be achieved, and manual crushing is necessary, greatly increasing labor intensity and reducing production efficiency.
-Inaccurate measurement: Blocked C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin cannot achieve uniform and accurate measurement during feeding, directly damaging the accuracy of downstream product formulas.
-Pre melting energy consumption increases: Large blocks of bestv C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin require longer melting time and higher energy consumption than standard particles, increasing production costs.
-Potential performance degradation: Local overheating may cause premature aging of some resins.
2. Oxidation and color deepening
(1) Cause: Heat, air (oxygen), and light are the three major culprits. Inappropriate storage conditions provide energy and reactants for oxidation reactions.
-High temperature and oxygen: For every 10 ° C increase in temperature, the chemical reaction rate approximately doubles. At high temperatures, C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin molecular chains (especially those rich in unsaturated double bonds and aromatic rings) undergo auto oxidation reactions upon contact with oxygen, generating chromophores such as peroxides and carbonyl compounds.
-Ultraviolet irradiation: Ultraviolet radiation in sunlight is an efficient photosensitizer that can directly break chemical bonds, trigger and accelerate photo oxidation reactions, and its destructive nature is more severe than thermal oxidation.
(2) Specific consequences:
-Significant color deepening: The best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin gradually changes from light yellow to amber, dark brown, or even black. Color is one of the key indicators for measuring the quality level of petroleum resin. Deepening the color means that the product is downgraded and cannot be used in fields that require high color, such as light colored adhesives, high-end inks, and light colored coatings.
-Performance degradation: The oxidation process is accompanied by the breakage and cross-linking of molecular chains, which can lead to a decrease in the resin's thickening effect, an increase in brittleness, and a decrease in compatibility.
3. Surface contamination and introduction of impurities
(1) Cause: Poor packaging sealing or outdoor storage in dusty and humid environments.
-Moisture intrusion: Although C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin is hydrophobic, its powder or small particles will absorb moisture and clump in a humid environment. More importantly, moisture can be introduced into downstream production systems, which may react with isocyanates to produce carbon dioxide in certain applications (such as polyurethane adhesives), causing product foaming and performance failure.
-Mechanical impurities mixed in: Foreign impurities such as dust, sand, and packaging debris enter the packaging with unclean air, becoming defect points in the final product, affecting the integrity of the adhesive film, smoothness of the coating film, etc.
2. Chemical property changes and final product defects
Physical changes are often superficial, but behind them are profound chemical changes that directly determine the functionality of the best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin in the final product.
1. Changes in molecular weight distribution and loss of performance
(1) Cause: Two main chemical changes will occur to the best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin under high temperature or oxidation environment for a long time: molecular chain fracture (leading to molecular weight reduction) and molecular chain cross-linking (leading to molecular weight increase and gel).
(2) Specific consequences:
-Decreased cohesive strength: Molecular chain breakage can significantly reduce the cohesive strength of the C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin as a tackifier, resulting in poor adhesion and easy peeling of the adhesive product.
-Poor compatibility: The polar groups generated by oxidation and the three-dimensional network structure formed by cross-linking will change the compatibility between the C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin and the main polymer (such as SBS, SIS rubber) and other additives, resulting in phase separation, manifested as adhesive oil, coating float, and decreased glossiness.
-Unstable viscosity: Changes in molecular weight distribution directly cause changes in the viscosity of best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin solutions or melts, posing great difficulties for downstream production process control.
2. Functional group changes and side reactions
(1) Cause: Oxidation reactions produce oxygen-containing functional groups such as peroxides, alcohols, ketones, and acids.
(2) Specific consequences:
-Accelerated aging: Newly generated peroxides are unstable and will continue to trigger and promote the degradation of the entire system, shortening the service life of the final product (such as tape, marking paint).
-Causing adverse side reactions: The increase in acidic groups may catalyze hydrolysis or condensation reactions of other components in downstream formulations, leading to premature product failure.
-Odor aggravation: Oxidative degradation can produce low molecular weight aldehydes and ketones, leading to unpleasant "halal" or irritating odors in resins and their products, which is a fatal flaw for applications such as sanitary materials and food packaging.
3. Security risks and storage hazards
Not meeting storage conditions not only affects product quality, but also poses a serious safety threat.
1. Rapid increase in fire risk
(1) Cause: C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin is a combustible solid, and its fire risk is closely related to temperature and management.
-Risk of spontaneous combustion: If the resin releases heat due to oxidation and the heat cannot be dissipated in a timely manner (such as excessive stacking or poor ventilation), the internal temperature may continue to accumulate, reaching the self ignition point and causing a fire.
-Dust explosion: If powdered C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin generates dust during storage and handling, and forms an explosive mixture with air, it is highly susceptible to powerful dust explosions when exposed to open flames, electric arcs, or high-temperature surfaces.
-Flash point and ignition point: High temperature environments cause the C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin surface to emit more flammable gases, making it more susceptible to ignition.
(2) Specific consequences: It may cause warehouse fires or even explosions, resulting in significant property damage, casualties, and environmental pollution.
2. Health and environmental hazards
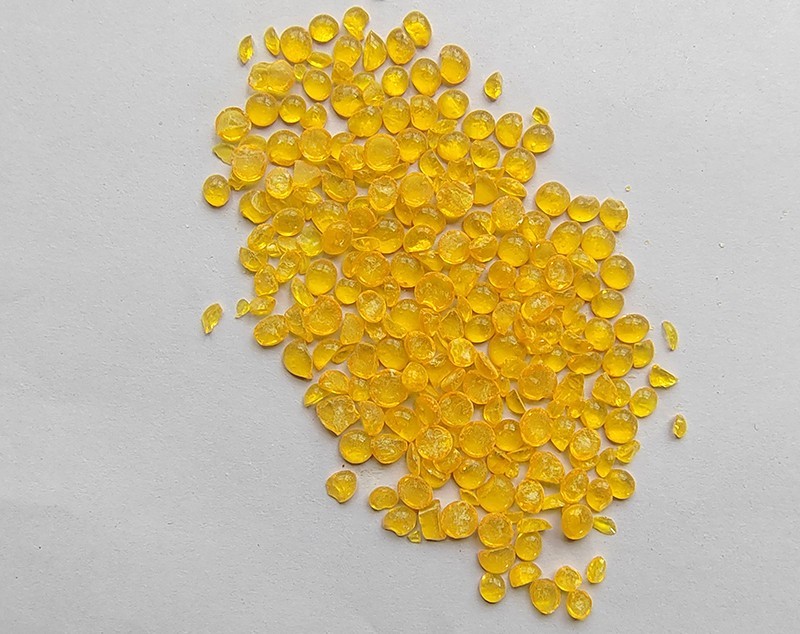

(1) Cause: Improper storage leading to the release or leakage of harmful substances.
-Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) Release: High temperatures can accelerate the volatilization of residual monomers, solvents, and degradation products in resins, polluting indoor air quality and endangering the health of warehouse personnel.
-Leakage pollution: If the packaging of molten best C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resin is damaged, it will leak to the ground or drainage system, causing soil and water pollution, and cleaning is extremely difficult.
4. Economic and commercial losses
Ultimately, all technical consequences will translate into tangible economic losses.
1. Product depreciation and scrapping: C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resins that have clumped or discolored need to be downgraded or directly scrapped, resulting in direct material losses.
2. Customer complaints and claims: Quality problems with downstream products produced using inferior C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resins can lead to customer complaints, returns, and even huge claims, seriously damaging the company's reputation.
3. Increased production costs: Processing agglomerated materials, adjusting problem formulas, increasing quality inspection frequency, etc. will all bring additional manpower, material resources, and time costs.
4. Legal and compliance risks: If a safety accident occurs due to improper storage, the enterprise will face regulatory penalties, production suspension for rectification, and even legal litigation.
For C9 thermally polymerized petroleum resins, their storage conditions are not optional "suggestions", but rather the "lifeline" that maintains their value and function. From the destruction of physical form to the decay of chemical structure, to severe safety hazards, any negligence in storage can trigger a domino effect failure from the warehouse to the production line. Therefore, establishing and strictly implementing a scientific warehouse management system, including constant temperature and humidity, light proof sealing, dust and fire prevention, first in first out, etc., is not only a necessary link in quality control, but also a core manifestation of enterprise risk management and fulfilling social responsibility.

 Language
▼
Language
▼




 Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province
Address:Linzi District,Zibo City,Shandong Province E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com
E-mail:wanbang@wanbangresin.com WhatsApp:+8615053337101
WhatsApp:+8615053337101